Domain Name System (DNS) is a network phone book of the internet. People commonly use it daily to carry out an array of online tasks. It forms the very basis of the internet and is a bunch of numbers to keep track of each device and location out there on the web. People access online information through these numbers. With the rapid increase of online devices, it has now taken the face of words. The words now form as the identity to each website and are easier to recall for people. Yet, you can still enter a specific IP address into a search bar to land on a website.
Best free and public DNS servers
Vivaldi Browser : New addition to android browser
Top 3 WordPress Alternatives
What is object storage? When to use and why?
Is blogging better than video content?
Reasons to use flat file CMS
Happy Birthday Internet
Top 3 YouTube Alternatives amid Indo-China Border Skirmish
Core Java Tutorial
Wix vs WordPress | Which is best?
Top Digital Advertising Trends in 2020
Ex-Foreign minister Sushma Swaraj passes away
Privacy focused search engine, DuckDuckGo again blocked in India?
Free India Public DNS Servers
Data Center Tiers: What Are They and Why Are They Important?
History Of Java
Coronavirus Pandemic Impact on Cyber Security
Top Benefits Of Learning Digital Marketing
Congress’s Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury’s blunder in LS debate
Top 7 Reasons for Starting an E-commerce Business
What is DNS? How does DNS works?
- July 18, 2020
- Posted by: webopediamaster
- Category: DNS
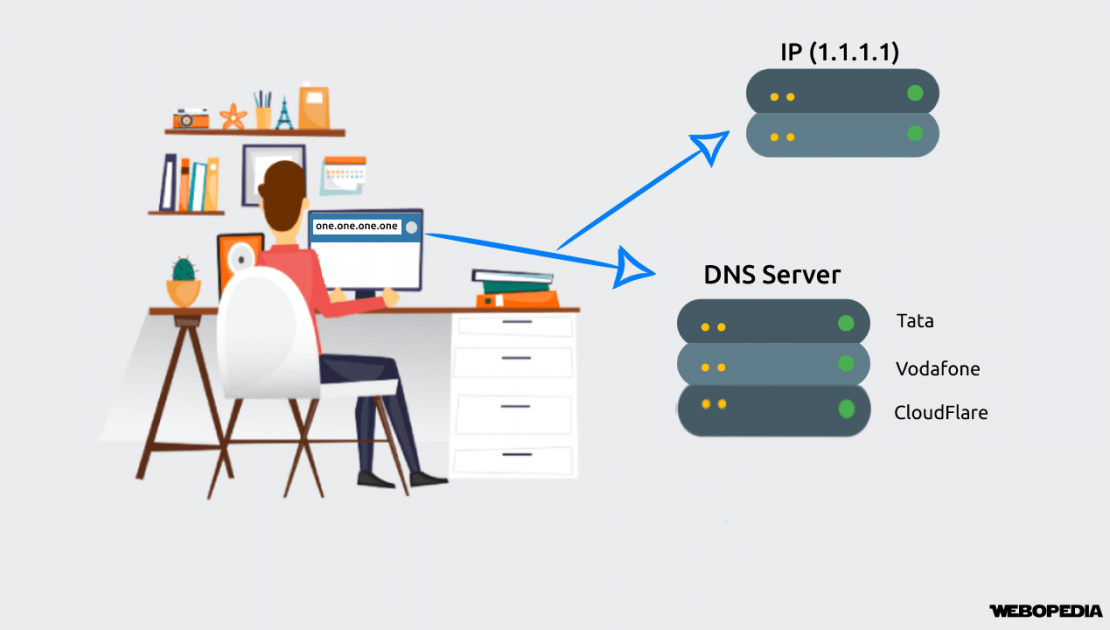
Working of a Domain Name Server (DNS)
DNS works on the principle of assigning an internet friendly IP address (Ex: 182.145.2.1 to a host like www.sample.com. The process is to assign an online address to each location on the web just like a physical address determines the address of a specific place.
A translator understands the user language and converts it to machine –friendly tongue to fetch correct results for the user. Let’s take a detailed look at how a DNS works behind the picture to resolve a user query.
The life cycle of a DNS travels four distinct steps to carry out the full process.
- DNS Recursor – The recursor acts as a librarian who is tasked with finding a specific book in the library. It is a server that accepts and processes the initial user queries. It then works further to resolve a user query.
- Root Nameserver – The root server is the first step in the rendering of a human-readable name into IP addresses. It works like an index of a library that keeps track of all the book addresses. You can easily use it to reach out to a specific location across the internet.
- TLD Nameserver – The server for the top level domain acts as a shelf of books in the library. It is the next step that seeks for a precise IP address and anchors the last section of a hostname.
- Authoritative Nameserver – It is the last step in the nameserver inquiry that behaves like a dictionary to simplify the details into a name. As per the access given to the record, it will return the asked hostname to the librarian (DNS Recursor) that started with the initial call.
We hope it is clear now, how a Domain Name Server works and its attributes. You can use free and private CloudFlare DNS to make your internet faster. Shoot your query if you still got any questions.